
Harald Bluetooth, a 10th-century Viking king, may seem an unlikely figure to be associated with the cutting-edge wireless technology we use today. However, his legacy extends far beyond the shores of medieval Scandinavia. In an unexpected turn of events, Harald Bluetooth has become synonymous with the ubiquitous wireless communication standard known as Bluetooth. This article explores the fascinating history of Harald Bluetooth, tracing his journey from a Norse ruler to an inspiration for modern technology, particularly in the realm of mobile communications.
THE VIKING KING
Harald Bluetooth, also known as Harald Gormsson, was born in the late 9th century, likely around 935 AD. He belonged to the Jelling dynasty and was the son of King Gorm the Old and Queen Thyra. Harald assumed the throne in 958 AD after the death of his father, marking the beginning of his reign as the King of Denmark.

Harald was a notable figure in Viking history, known for his ambitious campaigns and efforts to unite Denmark and parts of Norway under his rule. One of his significant achievements was the conversion of the Danes to Christianity. In the early 10th century, he embraced Christianity and played a pivotal role in spreading the new faith throughout his kingdom. Harald’s conversion to Christianity was a strategic move, aligning Denmark with the Christian powers of Europe and fostering diplomatic ties.
TURNING HIS BACK ON ODIN!?
The Jelling Stones, massive runestones erected by Harald in memory of his parents, serve as historical artifacts that commemorate his conversion and the Christianization of Denmark. The inscriptions on these stones not only highlight Harald’s achievements but also provide insights into the historical events of his time. This was a major step to move from the Pagan religion of Vikings ruled by Odin, Thor and Loki and moving towards the modern religious world.
DENMARK AND NORWAY MUST UNITE
Harald Bluetooth’s reign was marked by his efforts to consolidate power and expand his influence beyond the borders of Denmark. One of his most notable accomplishments was the unification of Denmark and parts of Norway. Through a combination of military conquests and political maneuvering, Harald succeeded in bringing disparate regions under his rule.

Harald’s control extended beyond the traditional Viking territories, and he established a North Sea Empire that included parts of Norway, Denmark, and southern Sweden. This unification laid the foundation for a more centralized and organized governance structure in the region.
BLUETOOTH TECHNOLOGY AND THE VIKING
While Harald Bluetooth is celebrated for his achievements in medieval politics and the spread of Christianity, his connection to modern technology is unexpected. The link between the Viking king and contemporary wireless communication can be traced back to the 20th century and the development of Bluetooth technology.
The term “Bluetooth” itself is not a random choice but a deliberate nod to Harald Bluetooth’s historical significance. In the late 1990s, as wireless communication technology was rapidly advancing, a group of technology companies, including Ericsson, Intel, and Nokia, collaborated to create a short-range wireless communication standard. The project needed a code name during development, and Jim Kardach, an Intel engineer, proposed “Bluetooth” as a temporary moniker.
The name Bluetooth was inspired by the historical connection and unification achieved by Harald Bluetooth in medieval Scandinavia. In the same spirit, the technology aimed to unite different devices, such as computers, phones, and peripherals, by enabling them to communicate wirelessly. The name stuck, and when the technology was officially introduced in 1999, it retained the historically significant name.
HARALDS LOGO LIVES!
The Bluetooth logo further reflects the historical inspiration behind the technology. The symbol combines the initials of Harald Bluetooth in the Nordic runes: “H” and “B.” The overlapping design represents the uniting of devices through wireless communication, drawing a direct parallel to Harald’s unification of diverse territories under his rule.
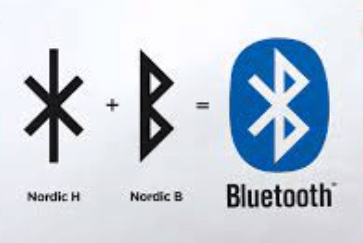
VIKING UNITING
The Bluetooth technology we use today is a wireless communication standard that allows devices to connect and exchange data over short distances. It operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band and uses a radio frequency to establish a secure and efficient communication link.
Bluetooth has evolved through various iterations, each offering improved features and capabilities. Initially developed for simple applications like hands-free headsets and file transfers, Bluetooth has become an integral part of our daily lives, supporting a wide range of devices such as smartphones, smartwatches, headphones, speakers, and even smart home appliances.
The technology enables seamless connectivity, allowing users to pair and share information between devices without the need for physical cables. Bluetooth has become particularly essential in the realm of mobile communications, enabling wireless audio streaming, data synchronization, and the creation of personal area networks.
Ericsson’s Role in Bluetooth Development
The story of Bluetooth’s development is closely tied to Ericsson, a Swedish multinational telecommunications company. Ericsson played a key role in the collaborative effort that led to the creation of Bluetooth technology. The company’s expertise in telecommunications and its commitment to innovation positioned it as a major contributor to the development and standardization of Bluetooth.
In 1994, Ericsson initiated the collaboration with other technology companies to explore the feasibility of short-range wireless communication. This initiative laid the groundwork for the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), a consortium of companies that continues to oversee the development and promotion of Bluetooth technology.
THE FIRST VIKING DEVICES, I MEAN BLUETOOTH DEVICES
The first Bluetooth-enabled devices were introduced to the market in the early 2000s. Ericsson, along with other industry leaders, showcased the potential of Bluetooth in practical applications. Mobile phones were among the early adopters of Bluetooth technology, allowing users to connect wirelessly to headsets, transfer files, and synchronize data between devices.
The success and widespread adoption of Bluetooth in mobile phones marked the beginning of its integration into various consumer electronics. As the technology advanced, Bluetooth became a standard feature in laptops, audio devices, automotive systems, and a myriad of other products, contributing to the seamless connectivity we experience today.
BLUETOOTH TODAY
Over the years, Bluetooth technology has continued to evolve, with each new version introducing improvements in speed, range, and energy efficiency. Bluetooth is now a ubiquitous feature in a wide range of devices, playing a crucial role in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has emerged as a power-efficient variant of the technology, enabling devices to communicate with minimal energy consumption. This has paved the way for the proliferation of connected devices, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other IoT devices that rely on low-power, short-range communication.
THE FUTURE OF BLUETOOTH
As technology advances, the role of Bluetooth is expected to expand further. With the advent of 5G technology, the integration of Bluetooth with other wireless standards is likely to enhance connectivity and create new possibilities for seamless device interactions.
Bluetooth Mesh, introduced in later versions of the standard, enables the creation of large-scale device networks, making it suitable for applications like smart lighting, industrial automation, and smart cities. The versatility and adaptability of Bluetooth ensure its continued relevance in the ever-evolving landscape of wireless communication.
ALL BECAUSE A VIKING CONVERTED
Harald Bluetooth, a Viking king of the 10th century, may not have anticipated the far-reaching impact his name would have on the world of technology. From his role in unifying medieval Scandinavia to becoming the inspiration for Bluetooth technology, Harald’s legacy has taken an unexpected turn through the centuries.
The story of Bluetooth serves as a fascinating intersection of history and technology, where ancient runes and Viking kings find a place in the digital age. As we wirelessly connect our devices and seamlessly transfer information in the 21st century, it’s worth remembering the historical roots that tie us to the past—a past that includes a Viking king named Harald Bluetooth.



Leave a comment